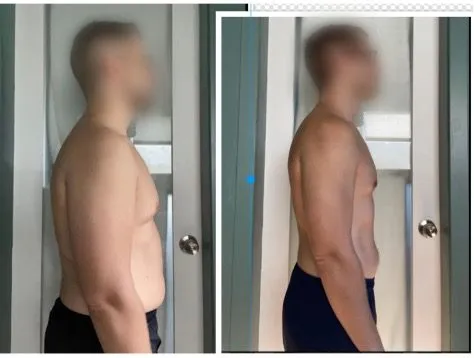
Introduction
Weight loss is a common goal for many people, but achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can be a challenging task. There are countless weight loss programs and strategies available, but not all of them are effective in the long term. The key to successful weight loss lies in understanding the science behind it and implementing evidence-based strategies that work.
The Role of Energy Balance
One of the fundamental principles of weight loss is energy balance. This concept is based on the simple equation that weight loss occurs when energy expenditure exceeds energy intake. In other words, you need to burn more calories than you consume in order to lose weight. This can be achieved through a combination of dietary changes and increased physical activity.
Dietary Changes
When it comes to weight loss, what you eat is just as important as how much you eat. A balanced and nutritious diet that is low in calories and high in nutrients is essential for successful weight loss. This includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoiding highly processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of added sugars and fats is also key.
Physical Activity
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity is crucial for weight loss. Exercise not only helps to burn calories, but it also improves overall health and wellbeing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Strength training exercises that build muscle mass can also help to boost metabolism and promote fat loss.
The Importance of Behavioral Change
Successful weight loss programs also focus on changing behaviors and habits that contribute to weight gain. This includes addressing emotional eating, stress management, sleep hygiene, and mindful eating. By identifying triggers and developing coping strategies, individuals can make sustainable changes to their lifestyle that support long-term weight loss.
Emotional Eating
Many people turn to food for comfort or as a coping mechanism for stress, boredom, or other emotions. Emotional eating can sabotage weight loss efforts and lead to unhealthy eating patterns. By learning to identify emotional triggers and finding alternative ways to cope, such as exercise, meditation, or talking to a therapist, individuals can break free from this cycle.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on weight and overall health. High levels of the stress hormone cortisol can lead to increased appetite, cravings for high-calorie foods, and abdominal fat storage. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature, can help to support weight loss goals.
Sleep Hygiene
Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep duration have been linked to weight gain and obesity. Lack of sleep can disrupt hunger hormones, increase cravings for unhealthy foods, and lower metabolism. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding screens before bed, can improve both sleep quality and weight loss outcomes.
Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly and without distractions, and savoring each bite. This practice can help individuals to better understand their body’s signals and prevent overeating. By being more mindful during meals and snacks, people can develop a healthier relationship with food and make more conscious choices that support weight loss.
The Role of Metabolism
Metabolism plays a key role in weight loss and weight maintenance. It refers to the processes by which the body converts food into energy and uses that energy to fuel bodily functions. A person’s metabolic rate is determined by a variety of factors, including age, gender, genetics, body composition, and activity level.
Basal Metabolic Rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the number of calories your body needs to maintain basic physiological functions at rest, such as breathing, circulation, and cell production. It accounts for the majority of the calories you burn each day. Factors that influence BMR include age, gender, body size, and muscle mass. Increasing muscle mass through strength training can help to boost BMR and support weight loss.
Thermic Effect of Food
The thermic effect of food (TEF) refers to the energy expenditure required to digest, absorb, and process the nutrients in the foods you eat. Different macronutrients have varying thermic effects, with protein requiring the most energy to metabolize, followed by carbohydrates and fats. Including a balance of all three macronutrients in your diet can help to maximize TEF and support weight loss.
Physical Activity Level
Physical activity plays a significant role in metabolism and weight loss. Exercise not only burns calories during the activity itself but also increases metabolism for hours afterward. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and strength training are particularly effective for boosting metabolism and promoting fat loss. Incorporating both cardio and strength training into your fitness routine can help to maximize weight loss results.
The Science of Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the three main components of food that provide energy: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each macronutrient plays a unique role in the body and has different effects on metabolism, hunger, and weight loss.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy and are found in foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by the body for fuel. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and starchy vegetables, provide sustained energy and fiber, while simple carbohydrates, like sugars and refined grains, can lead to blood sugar spikes and cravings. Balancing carbohydrate intake with fiber and protein can help to stabilize blood sugar levels and support weight loss.
ProteinsProteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, muscles, and organs. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. Protein-rich foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts are important for maintaining muscle mass, promoting satiety, and supporting weight loss. Including protein with each meal and snack can help to control hunger, regulate blood sugar, and preserve lean body mass during weight loss.
Fats
Fats are essential for hormone production, brain function, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, are important for overall health and can support weight loss when consumed in moderation. Avoiding trans fats and minimizing saturated fats from processed and fried foods is important for heart health and weight management. Including a balance of unsaturated fats in your diet can help to improve cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss.
The Role of Hormones
Hormones play a crucial role in weight regulation and metabolism. They influence appetite, energy expenditure, fat storage, and muscle mass. Imbalances in hormones like insulin, leptin, ghrelin, cortisol, and thyroid hormones can impact weight loss efforts and make it more challenging to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels by transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy. When insulin levels are elevated, fat storage is promoted, and weight loss can be hindered. Balancing blood sugar levels through a diet rich in whole foods, low in added sugars, and high in fiber can help to improve insulin sensitivity and support weight loss.
Leptin and Ghrelin
Leptin and ghrelin are hormones that regulate hunger and satiety. Leptin signals the brain when you are full, while ghrelin stimulates appetite and promotes food intake. Disruptions in these hormones can lead to overeating and weight gain. Eating balanced meals, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can help to regulate leptin and ghrelin levels and support healthy eating habits.
Cortisol
Cortisol is known as the stress hormone and plays a role in metabolism, inflammation, and fat storage. Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can promote abdominal fat accumulation and weight gain. Finding effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises, can help to lower cortisol levels and support weight loss.
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones, such as T3 and T4, regulate metabolism and energy production. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can slow metabolism and lead to weight gain, while an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can increase metabolism and result in weight loss. Thyroid disorders can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes to support healthy weight management.
Conclusion
Successful weight loss programs are based on the principles of energy balance, behavioral change, metabolism, macronutrients, and hormones. By understanding the science behind weight loss and implementing evidence-based strategies, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight in the long term. By focusing on dietary changes, physical activity, behavior modification, and hormonal balance, people can make sustainable lifestyle changes that support their weight loss goals. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help to develop a personalized weight loss plan that is safe, effective, and tailored to individual needs.