Reviewed by means of Brian St. Pierre, MS, RD and Helen Kollias, PhD
It’s like my ideas have been below a collection of rubbish.
On a Friday night time, as my husband and I attempted to determine the place to devour, a regular dialog would walk like this:
Me: Do you need to walk to that eating place?
Him: What eating place?
Me: I will be able to’t recall to mind the identify. We’ve eaten there sooner than. It’s that park with the peanut shells at the flooring? It’s later to… You understand… It’s on that highway the place we impaired to whip the canine to the vet. Have you learnt the only I’m speaking about??
It used to be as though sure main points were given misplaced in a collection of sludge within the deep recesses of my mind. After, hours upcoming, the main points would depart, and I’d yell into an unfilled room…
“Texas Roadhouse!”
Sludginess with correct nouns is standard for family who’re middle-aged and past.
Alternatively, what gave the look to be going down to me, an increasing number of in my past due 40s and early 50s, felt a ways from standard.
Now not simplest may I by no means appear to spit out the names of numerous eating places or family or books or motion pictures or such a lot of alternative issues, however my mind used to be additionally pooping out all over the workday.
I’d take a seat in entrance of my display screen, stare at a report, and can myself to do one thing optimistic with my fingertips. The whole lot gave the impression unclear, like the ones first few moments within the morning whilst you’re wakeful plethora to show off the alarm however too sleepy to do ordinary math.
I had my just right moments, in most cases within the morning, after I tried to bundle 8 hours of writing into the 2 or 3 hours I possessed psychological readability.
On my worst days, alternatively, I aroused from sleep with a haze I by no means controlled to shake. Paintings used to be a non-starter. Nor did I’ve plethora bandwidth to learn, or do a lot of the rest, in reality.
I sought clinical recommendation.
3 healthcare pros beneficial antidepressants. I attempted one, and felt even worse. I attempted every other. I attempted but every other at a better dose. Nonetheless, I felt like a zombie. Every other skilled gave me a sound asleep tablet. It left me feeling much more drugged.
Any individual examined my thyroid. There used to be not anything unsuitable with it. Nor used to be I anemic. I attempted dietary supplements, mushroom espresso, and with regards to any product with the guarantee “think” someplace on its label.
In spite of everything, later just about two years of ocular a revolving door of docs, I made an appointment with a gynecologist for my annually examination. I discussed vaginal dryness. That data induced her to invite a story of questions that had not anything to do with my undercarriage. How used to be my amusement? Temper? Power ranges? Was once I experiencing sizzling flashes? How about mind fog?
“Funny you should mention brain fog,” I stated in my familiar unclear monotone. “I feel like I’m barely alive.”
By means of the top of the seek advice from, I understood that I’d most likely by no means had despair.
What I “had” used to be menopause.
My gynecologist despatched me house with prescriptions for estradiol and progesterone.
Inside of days, it used to be as though somebody had flipped a transfer.
I may suppose once more. I may kind phrases once more. I may practice conversations. I may paintings week midday.
And, for the primary generation in years, I may amusement greater than two hours with out waking.
Now, menopause isn’t a clinical situation.
Neither is it a problem.
In lieu, like puberty, it’s a era level—a transitional age to be exact.
When you’ve long gone 12 consecutive months with no duration, you’ve reached menopause. And from that age onwards, you’re formally “postmenopausal.”
As ladies means this transitional age, hormone ranges range and fall, triggering dozens of signs. Weight gain and lowered intercourse power get a batch of consideration.
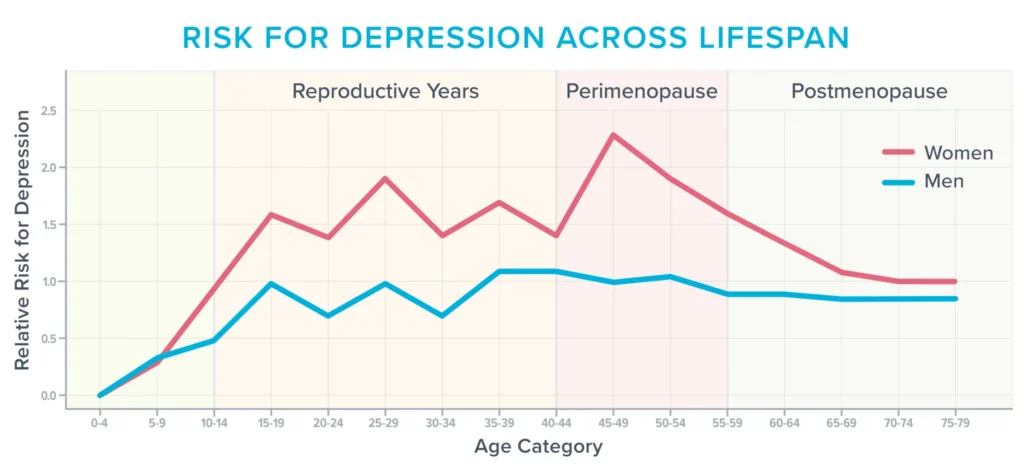
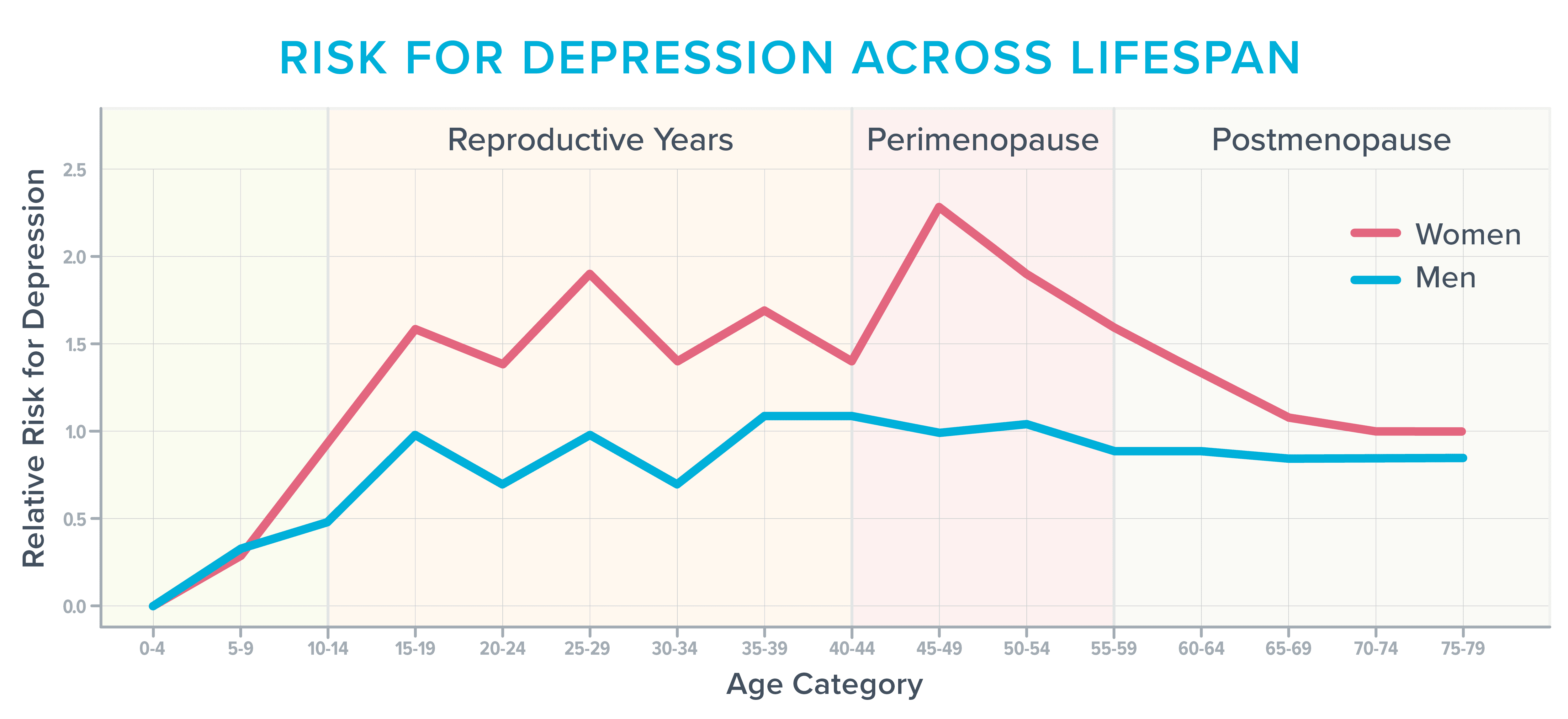
Alternatively, all over and later menopause, more or less 40 % of ladies record larger irritability, temper swings, anxiousness, fatigue, and hassle concentrating, consistent with the American Faculty of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.1 2 As please see symbol presentations, it’s additionally probably the most susceptible occasions in a girl’s era to build despair,3 specifically in the event that they’ve struggled within the week with it sooner than.
Earlier than foundation hormones, I steadily discovered myself sobbing for incorrect explanation why. Alternative occasions, the arena’s stimuli felt too… stimulating.
Customary on a regular basis sounds—like the excitement of visitors or family on the mall—actually harm. I used to be jumpy and irritable and felt fearful about statuses that had by no means troubled me within the week, corresponding to using over bridges or thru development.
It’s now not totally view through what drives those cognitive and emotional signs.
Fluctuating hormone ranges most likely play games a task, as do standard age-related adjustments within the mind.
As well as, all over this level of era, ladies steadily do business in with a number of problems that siphon cognitive capability quicker than a thirsty vampire drains a carotid.
All through their 40s and 50s, as an example, many ladies have reached the height in their careers, with duties that practice them house and store them up at night time. They can be parenting angst-filled teenagers, taking good care of growing older folks, adjusting to an unfilled nest, wondering their marriage, or seeking to wrap their warehouse account across the original remark from the school bursar or sanatorium billing branch.
Alternatively, one of the crucial lesser-known and mentioned triggers for cognitive discontent has not anything to do with growing older or era rigidity and the whole thing to do with that hallmark menopausal symptom: the new flash.
Anatomy of a sizzling flash
Scorching flashes, which occur all over the life, and night time sweats, which happen at night time, fall below the division of vasomotor signs. (The guarantee “vasomotor” refers back to the constriction or dilation of blood vessels which, in flip, can affect the whole thing from blood drive to sweating.)
All through a sizzling flash or night time sweat, norepinephrine and cortisol ranges be on one?s feet. Blood vessels dilate in an effort to release warmth. Blood drive and center charge build up.
Relying at the severity of the new flash, your pores and skin would possibly redden as sensations of heat unfold thru your face, neck, and chest.
It’s possible you’ll sweat, enjoy center palpitations, or really feel fearful, drained, or fall down.4
It’s now not totally view through why sizzling flashes abbreviate up round menopause.
Consistent with one idea, falling estrogen ranges have an effect on the hypothalamus, the department of the mind interested by temperature law. The mind’s interior thermostat will get wonky and infrequently thinks your physique is just too sizzling or chilly (when it’s now not).
How vasomotor signs trade the mind
For a few years, professionals considered vasomotor signs as mere inconveniences or resources of embarrassment.
(To be fair, so did I. All through all of the ones fruitless visits to numerous healthcare pros, it by no means passed off to me to say them.)
Alternatively, an expanding physique of study has seen that sizzling flashes might do greater than assemble us uncomfortable or pressure us to switch our sheets in the midst of the night time.
They may additionally have an effect on our blood vessels and brains—and now not for the simpler.5 Because of this, increasingly professionals now imagine vasomotor signs to be a treatable clinical situation.6 7 8
Scorching flashes and mind lesions
In a single find out about, researchers requested 226 ladies to put on displays that tracked once they have been experiencing a sizzling flash. The ladies additionally underwent magnetic voice imaging (MRI), crammed out amusement diaries, and wore smartwatches that recorded how steadily they woke at night time.9
As researchers appeared on the mind pictures received from ladies who skilled essentially the most sizzling flashes, they spotted an plenty of patchy farmlands referred to as whole-brain white subject intensities.
Those lesions have been as soon as considered a regular aftereffect of growing older. Alternatively, neuroscientists now consider that the presence of whole-brain white subject intensities is predictive of pace cognitive subside.
Nation with an plenty of those mind lesions are two times as more likely to get identified with dementia and 3 times as more likely to have a pace stroke.10
The blood vessel connection
It’s idea that the larger presence of whole-brain white subject intensities might stem, partially, from adjustments taking park within the blood vessels that feed the mind.
A 3-year find out about of 492 ladies helps that idea. It progressive that ladies who skilled common sizzling flashes additionally tended to enjoy dangerous adjustments of their blood vessels, corresponding to an incapacity to dilate to deal with larger blood current.11
Alternative study has related common sizzling flashes with will increase in please see:
- Thickening within the carotid arteries that offer blood to the mind, face, and neck12
- Frame weighty
- Overall and LDL ldl cholesterol
- Insulin resistance13 14 15 16
The amusement connection
Along with immediately affecting the blood vessels, common sizzling flashes may additionally have an effect on the mind by means of annoying amusement.17
Curiously, many ladies don’t essentially know that sizzling flashes are annoying their amusement.
They are going to in lieu—as I did—think they’ve insomnia or amusement apnea.
That’s as a result of night time sweats aren’t all the time torrid.
By means of the generation a surge in cortisol and norepinephrine jolts a girl wakeful, the hotness of the flash will have dissipated. So, it will probably really feel as though she’s again and again waking, over and over and over, for incorrect discernable explanation why.
Those common awakenings might intrude with the mind’s talent to consolidate reminiscences, metabolize toxins, and collect all of the names, dates, and details one encounters day-to-day.
It will probably additionally govern to misplaced connectivity within the hippocampus, part of the mind that’s remarkable for studying and reminiscence.
Diversion loss additionally approach the amygdala, part of the mind interested by emotion, turns into extra reactive, inflicting family to really feel extra simply stressed out, fearful, irritable, annoyed, or wrathful.18 19
All of those mind adjustments can eager in later simply days to a future of misplaced amusement. So, consider what occurs whilst you’ve been waking over and over—for years.
Why it may be crisp to get assistance
To diagnose despair, healthcare pros worth a device referred to as the Affected person Fitness Questionnaire (PHQ-9) despair scale. If you happen to test off 4 of the 9 signs at the scale, you’re thought to be depressed.
Alternatively, 4 of the indications at the tick list additionally overlap with the indications of menopause-related amusement deprivation:
- Minute hobby or amusement in doing issues
- Bother falling or staying asleep
- Feeling drained or having slight power
- Bother focusing on issues, corresponding to studying the newspaper or staring at tv
Test off the ones 4 pieces, and also you may well be identified with despair, despite the fact that what’s in reality unwell you is the combat with amusement you’ve been waging because you became 47.
A shortage of menopause-specific coaching
Every other sickness: On surveys, 80 % of clinical citizens admit they really feel “barely comfortable” speaking about menopause.20 As well as, few residency systems—together with ob-gyn residency systems—trade in coaching in it.21
Given the above, it’s incorrect miracle such a lot of healthcare pros by no means suppose to invite about sizzling flashes or amusement disturbances when family like me display up complaining of fatigue, shortage of gumption, and an incapacity to center of attention.
As well as, even if it’s view through that vasomotor signs are to cognitive and emotional signs, many healthcare pros nonetheless shy clear of prescribing menopausal hormone treatment (often known as hormone substitute treatment, or HRT), steadily telling ladies that supplemental hormones are “not safe” or “too risky.”
Those pros are practising what Michigan-based menopause-trained gynecologist Jerrold H. Weinberg, MD, yells “defensive medicine.”
“It’s one of the first reflexes doctors have when they recommend a treatment,” says Dr. Weinberg. “They worry they’re going to get sued.”
What the study in fact says about hormone treatment
Those worries are in accordance with study achieved a number of a long time in the past that related the worth of sure forms of hormones with a somewhat larger possibility of growing breast most cancers or stroke.22
Alternatively, consistent with newer study, that mini larger possibility turns out to rely on a number of alternative elements, corresponding to date, dose, the kind of hormonal preparation, and the length of hormone worth.23 24
So long as you’re more youthful than 60 and feature been postmenopausal for fewer than 10 years, many professionals now say the advantages outweigh the dangers for ladies with average to dreadful menopausal signs.25
It’s additionally counterbalanced by means of fitness advantages corresponding to lowered possibility of growing Alzheimer’s problem or osteoporosis, says Dr. Weinberg, who confirms the fitness advantages of menopause hormone treatment a ways outweigh the dangers for most girls.
As a result of some antidepressants can elevate temper, make stronger amusement, and leave sizzling flashes, some healthcare pros flip to them in lieu of menopause hormone treatment. As with every medication, antidepressants have their very own listing of unwanted side effects. Alternatively, for somebody practising defensive medication, they steadily appear to be a more secure wager, says Dr. Weinberg.26 27 28
Methods to suggest to your fitness
If you happen to or your consumer are on what turns out like a endless quest to discover a healthcare skilled who understands menopause, worth please see recommendation from Dr. Weinberg and Helen Kollias, PhD, a professional on body structure and molecular biology and science marketing consultant at Precision Diet and Women Long gone Robust.
▶ Search assist from a menopause-trained fitness skilled.
Generally, those pros listing this coaching and hobby of their bio. For instance, they could listing “menopause” as an department of center of attention.
You’ll be able to additionally seek this database for practitioners who’ve earned a certification from the Menopause Folk.
▶ Record your signs.
Incrible them ailing. That means, if you are feeling foggy or worried all over your appointment, you’ll incline in your notes.
This knowledge too can assistance you pass judgement on whether or not MHT or every other medication is operating. In line with your symptom information, you and your healthcare skilled might make a decision to modify to another medication or trade your dose.
Imagine monitoring:
- How steadily you get sizzling flashes
- The selection of hours in a regular life you end up scuffling with mind fog
- How steadily you enjoy fatigue, anxiousness, infuriate, or some alternative symptom
- How steadily you get up at night time
▶ Be as particular as you’ll all over your appointment.
Announcing one thing like “I don’t sleep well,” is much less more likely to get you the proper of assistance than pronouncing, “During the past seven days, I’ve only gotten four uninterrupted hours once. I wake, on average, five times a night. On a typical night, my longest stretch of sleep is three hours.”
If you happen to worth a smartwatch, come in a position to stir up your fitness app, so your healthcare skilled can see the information.
▶ Communicate in regards to the execs and cons of remedy.
There’s an idea in medication referred to as “shared decision-making.” A part of that procedure comes to frank discussions about the advantages and dangers of a given remedy. After, sufferers and clinicians paintings in combination to assemble choices in accordance with the ones advantages and dangers.
Many healthcare networks inspire clinicians to worth shared decision-making, as it kind of feels to leave affected person lawsuits in addition to malpractice complaints.29 30
Because of this, shared decision-making can assistance shift a healthcare skilled out of the “defensive medicine” mindset.
It’s possible you’ll ask questions like:
- “I’m interested in seeing if menopausal hormone therapy might be helpful. Could we discuss if I’m a good candidate?”
- “I’ve read that menopausal hormone therapy could slightly increase my risk of breast cancer. Could you help me understand my personal breast cancer risk based on my family history, age, body weight, and lifestyle?”
- “Osteoporosis runs in my family, as does dementia. I’ve heard that menopausal hormone therapy might help to reduce the risk for both, in addition to helping me sleep. Could you help me weigh the pros and cons?”
Methods to make stronger psychological and emotional fitness all over menopause: 9 way of life methods
The way of life behavior that make stronger psychological and emotional fitness all over menopause aren’t extraordinarily other from the way of life behavior that make stronger general fitness—for any individual, at any level of era.
Alternative than averting caffeine, alcohol, and highly spiced or sizzling meals, there’s incorrect particular vitamin for family with vasomotor signs. (And by means of the way in which, tofu and alternative soy merchandise don’t appear to assistance with vasomotor signs up to as soon as idea30—despite the fact that they’re nonetheless nourishing.)
Technique #1: Incline into basic fitness methods.
Wholesome behaviors don’t essentially trade all over center date.
Diet, bodily job, rigidity control, amusement, social connectedness, and a way of objective subject simply as a lot all over the menopausal transition as they do once we’re more youthful. Alternatively, those basics are much more remarkable to dial in as era progresses.
So imagine:
- Are you environment apart plethora generation for amusement and extra?
- Are you bodily lively?
- Are you consuming a vitamin that’s most commonly minimally processed and stuffed with brightly coloured create, wholesome fat, incline protein, fibrous greens, and legumes?
- Do you often fix with alternative people in ways in which assistance you buffer rigidity and really feel supported?
- Do you in finding techniques to enjoy surprise, pleasure, interest, diversion, and objective?
If you happen to responded “no” to a few or all of the ones questions, imagine why this is. What’s preventing you? How would possibly you take away limitations or shore up help to assemble the ones basics more uncomplicated?
Technique #2: Experiment with creatine.
Along with serving to to blunt age- and hormone-related losses in muscle and bone aggregate, creatine may additionally assistance bolster temper and mind serve as pace lowering psychological fatigue.
It additionally turns out to counter one of the vital unintended effects of amusement deprivation. 32 33 Analysis presentations a day-to-day dose of five to 7 grams of creatine monohydrate is efficacious.
Technique #3: Get ordinary about luminous publicity.
Along with serving to you are feeling alert, daylight is helping to eager the interior clock to your mind that makes you sleepy at night time and spunky within the morning. Morning and past due afternoon luminous publicity appear specifically potent.
In a find out about of 103 family, publicity to morning daylight predicted higher amusement detail please see night time. When family spent generation outside within the mornings, they fell asleep extra briefly, slept longer, and skilled fewer awakenings please see night.34
Daylight may additionally make stronger temper and focus.35
Technique #4: Exit more uncomplicated on the health club.
If you happen to’re already used out, lengthy, intense workout classes will most likely assemble you are feeling worse.
For one, accidents abbreviate up a lot more simply at center date than all over our 20s and 30s. As well as, it takes longer to get better between classes.36
Story too many overly zealous workout routines too akin in combination, and also you’ll now not simplest most likely begin to really feel achy but in addition extra irritable, traumatic, and drained.
Alternatively, similar to a chilly bathe, scale down bursts of workout might assistance you to really feel alert all over the life.
If you happen to’re falling asleep at your table, inspire your self to whip scale down motion breaks corresponding to a 5- or 10-minute exit outside or a snappy eager of pushups or squats.
As well as, you might in finding tender workout—corresponding to yoga or stretching—is helping you inactivity sooner than mattress. Simply don’t assemble it too intense, otherwise you’ll cause a leave of adrenaline.
On every occasion you workout, track into how your physique feels, particularly later a specifically malicious night time of amusement.
We’re now not pronouncing you will have to by no means workout vigorously or attempt to overcome your lifting PRs. Alternatively, relying in your amusement and fix, chances are you’ll wish to pare issues again, particularly when you’ve historically collision the health club crisp.
You’ll be able to nonetheless do intense classes—simply stability them out with extra average classes, in addition to proportionate fix.
Relying on how you are feeling, chances are you’ll make a decision to walk all out, as familiar.
Alternatively, you may additionally make a decision to do a zone 2 training session in lieu of an intense run. Or, when you’re resistance coaching, chances are you’ll nonetheless do your deliberate consultation, however leave the selection of units, reps, or quantity lifted.
Technique #5: Examine Cognitive Habits Treatment for Insomnia (CBT-I).
This research-based treatment for insomnia can assistance you build abilities and psychological reframes that inspire pitch amusement.
For instance, a CBT-I therapist will assistance you build the ability of having up on the identical generation each and every life, without reference to how badly you slept (or didn’t amusement) the night time sooner than.
(Learn extra: Three CBT-I skills that can transform how you sleep.)
Technique #6: Get actual about rigidity.
You would possibly not have the power (or need) to do the whole thing you probably did whilst you have been more youthful. (While you have been 36, your day-to-day tick list defied generation and dimension.)
Consequently, chances are you’ll have the benefit of having a look significantly at your tide duties to peer which of them you’ll abridge or downsize. For a number of days, observe the way you spend your generation and bandwidth. After, analyze your information.
Ask your self:
- Is that this the way you really wish to spend your generation and effort?
- Does your tide agenda permit you to extra, get better, and have a tendency on your personal wishes? Or, do you spend just about your whole generation and effort taking good care of and offering for others?
- What adjustments may you assemble to prioritize extra and fix?
If you happen to’re a lecturer, worth the Wheel of Stress Assessment to assistance purchasers establish other dimensions in their era that may well be draining their psychological and emotional capability. (While you know in particular the place your rigidity is coming from, you might have a greater prospect of resolving it.)
If it’s calls for from alternative family that forbid you from prioritizing self-care and fix, chances are you’ll love to learn: How saying “no” can seriously change your life.
Technique #7: Experiment with cooling generation.
It’s possible you’ll in finding you amusement higher and enjoy fewer night time sweats when you amusement in a cooler climate.
Struggle turning ailing the thermostat a few levels, the use of a fan, or making an investment in an electrical cooling bed abode.
Technique #8: Hurry common breaks.
When you are feeling the fog to enter your mind, it’s probably not you’ll be doing “your best work” anyway.
So, for a restrain of generation—say, 20 mins—allow your self to do not anything. It’s possible you’ll:
- Inactivity with a chilly beverage
- Cuddle with a puppy
- Gaze out a window
- Sit down outside pace paying attention to the birds
- Name a pal
If you want a snappy “refresh,” you’ll additionally attempt a 5-minute mind-body scan.
Get your physique right into a at ease place. For instance, chances are you’ll worth the yoga “legs up the wall” pose or lie ailing and park a pillow below your knees.
After, akin your visible and convey your consideration to bodily sensations to your physique. Get started at your head, and paintings your means ailing on your feet.
Don’t pass judgement on or sprint to switch the rest. Simply follow, like a scientist. You’ll be able to additionally scan your intellect, as an example, by means of noticing ideas.
While you’ve finished the scan, imagine:
- What are you feeling bodily?
- What are you feeling emotionally?
- What are you pondering?
You don’t must “do” the rest with the guidelines you discover, simply realize.
Technique #9: Apply a vitamin that promotes wholesome movement.
The meals that offer protection to the blood vessels round your center too can offer protection to the blood vessels to your mind.
For instance, each the MIND and Mediterranean diets are related to a discounted possibility of Alzheimer’s problem and despair.37 38 Those consuming patterns are ffluent in greens, fruit, complete grains, olives, beans, fish, and alternative minimally-processed complete meals.
As well as, nitrate-rich meals like beets and black, leafy vegetables might assistance to dilate blood vessels, briefly making improvements to reminiscence by means of serving to extra blood to succeed in the mind.39 40
(For extra on how our vitamin can help mind serve as and emotional law, learn: Nutrition and mental health: What (and how) to eat)
The upside of menopause
It’s irritating when you are feeling like you’ll’t do all of it.
Imagine me. I do know.
Alternatively, this level of era items a invisible alternative, forcing you to re-examine what’s maximum remarkable.
Earlier than happening hormones, as my talent to kind coherent phrases and words reduced, I used to be pressured to invite an remarkable query:
Do I in reality want to be doing this?
It used to be extra of an existential query than a career-related one, and it allowed me to think again how I sought after to spend my restricted psychological assets.
For the reason that I used to be self-employed, I didn’t in fact want to be running 8 hours a life. That used to be a present, wasn’t it?
Perhaps I additionally didn’t want to cook dinner dinner six nights out of 7. Perhaps the recipes I selected might be simplified, too.
In spite of everything, perhaps pronouncing “no” a batch extra steadily and with out remorseful about would permit me to proceed to mention sure to the issues that mattered maximum.
Such things as visiting my growing older folks.
And selecting up the telephone each time my child referred to as from school.
Or assembly a pal for a meandering exit round the town.
Because of the hormones and era tweaks, I now have power once more. I’m additionally clear-headed many of the generation. Alternatively, I nonetheless generally tend to finish my paintings life round 3 p.m.
Why?
As a result of I will be able to, and I wish to.
References
Click on right here to view the guidelines resources referenced on this article.
Source link